Money doesn’t just grow on trees — it grows with a plan.
Most people dream about financial freedom: buying a home, traveling the world, or retiring early. But dreams without a plan are just wishes. That’s where SMART financial goals come in — a framework that helps turn vague wishes into clear, achievable milestones.
This ultimate guide will walk you through how to set SMART financial goals, examples of short-term and long-term goals, and practical steps to make them a reality. Whether you’re saving your first $1,000 or planning for a million-dollar retirement, this guide will help you take control of your money with clarity and purpose.
What Are SMART Financial Goals?
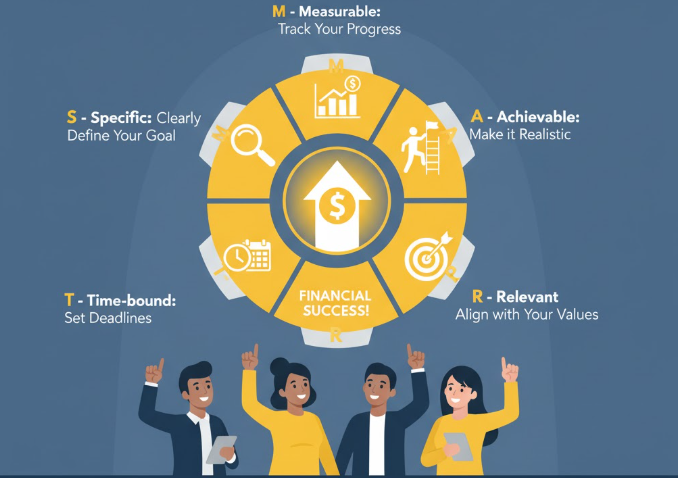
SMART is an acronym that stands for:
| Letter | Meaning | Key Focus |
|---|---|---|
| S | Specific | Clear and well-defined |
| M | Measurable | Trackable with numbers or milestones |
| A | Achievable | Realistic and within reach |
| R | Relevant | Aligned with your life priorities |
| T | Time-bound | Set within a deadline |
When you apply this formula to your finances, you create goals that are both motivating and manageable.
For example:
❌ “I want to save money.”
✅ “I will save $5,000 in the next 12 months by cutting dining out and automating savings of $420 per month.”
See the difference?
The second goal is specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound — and therefore far more powerful.
Why Setting SMART Financial Goals Matters
Before diving into how to create SMART goals, it’s important to understand why they matter. Financial success isn’t about luck — it’s about direction.
1. Clarity and Focus
When you have a SMART goal, you know exactly what you’re working toward. You stop guessing and start planning.
2. Motivation and Accountability
Specific goals keep you motivated. You can measure progress, celebrate small wins, and stay accountable.
3. Better Financial Habits
SMART goals naturally lead to better money habits like budgeting, saving, and tracking expenses.
4. Reduced Stress
Money is one of the top causes of stress. A clear plan helps replace anxiety with confidence.
Step-by-Step Process to Set SMART Financial Goals
Let’s walk through how to build your own SMART financial plan, step by step.
Step 1: Start with Your “Why”
Before you set any number, understand your motivation.
Ask yourself:
-
What matters most to me financially?
-
Why do I want to achieve this goal?
-
How will it improve my life?
Your “why” keeps you going when saving or paying off debt feels hard.
Example:
-
I want to save $10,000 for an emergency fund because I don’t want financial stress during unexpected events.
Step 2: Be Specific
General goals like “I want to save more” don’t work.
Instead, specify:
-
What you want to achieve
-
How much it will cost
-
How you’ll get there
Example:
“Save $3,000 in six months to cover three months of living expenses.”
This tells you exactly what success looks like.
Step 3: Make It Measurable
You can’t improve what you can’t measure.
Attach a number to your goal so you can track your progress.
Example:
If you want to pay off debt, specify:
“Pay off $6,000 in credit card debt by paying $500 monthly for 12 months.”
You’ll easily see how close you are to the finish line each month.
Step 4: Keep It Achievable
Ambition is great, but goals must also be realistic.
If you earn $2,000 a month, saving $1,500 isn’t sustainable. Instead, choose an amount that challenges you but doesn’t overwhelm you.
Pro Tip:
Start small and increase over time. Once you build consistency, even small wins lead to massive progress.
Step 5: Ensure It’s Relevant
Your goal should align with your current stage of life and priorities.
For example:
-
If you’re a college student, building an emergency fund or paying off student loans might be most relevant.
-
If you’re a parent, saving for your child’s education could be a higher priority.
Ask:
“Does this goal move me closer to the life I want?”
Step 6: Set a Time Limit
Deadlines drive action.
A goal without a timeline is just a dream.
Example:
“Save $10,000 in 12 months” gives you a clear timeline and pace.
You can even break it down monthly:
$10,000 ÷ 12 = $833 per month.
This turns a big goal into smaller, doable chunks.
Examples of SMART Financial Goals
Here are examples of SMART goals for different life stages and priorities:
| Goal Type | Example |
|---|---|
| Short-Term | Save $2,000 in 6 months for a vacation by transferring $333 monthly into a savings account. |
| Medium-Term | Pay off $10,000 student loan in 2 years by paying $417 per month. |
| Long-Term | Build a $200,000 retirement fund in 20 years by investing $500 monthly in mutual funds. |
| Lifestyle Goal | Save $5,000 in 10 months to upgrade your car. |
| Family Goal | Save $30,000 for a home down payment within 3 years. |
Each of these goals is measurable, realistic, and time-bound — the perfect recipe for success.
Breaking Down Financial Goals by Time Frame
Let’s categorize your goals so you can prioritize them effectively.
| Time Frame | Example Goals | Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Short-Term (0–2 years) | Emergency fund, credit card debt, small vacation fund | Budgeting, cutting expenses, automating savings |
| Mid-Term (2–5 years) | Home down payment, car purchase, higher education | High-interest savings, certificates of deposit (CDs), side hustles |
| Long-Term (5+ years) | Retirement, investment portfolio, child’s college fund | Stocks, real estate, retirement accounts (401k, IRA) |
By separating your goals this way, you can decide how to allocate your income wisely.
Visual Infographic: SMART Financial Goal Pyramid
(Imagine a pyramid chart)
Top (Long-Term Goals): Retirement, Financial Freedom
Middle (Medium-Term Goals): Home, Car, Education
Bottom (Short-Term Goals): Emergency Fund, Debt Repayment, Budgeting Discipline
Each layer supports the next. Without the foundation of short-term stability, long-term goals are harder to achieve.
How to Track and Monitor Your SMART Goals
Tracking progress keeps you motivated and accountable.
1. Use a Goal Tracker Spreadsheet
Create a simple sheet with columns for:
-
Goal Name
-
Target Amount
-
Deadline
-
Monthly Contribution
-
Current Balance
-
% Completed
2. Automate Your Savings
Set up automatic transfers from your checking to savings. You’ll save money without even thinking about it.
3. Review Monthly
Once a month, check your progress and adjust if needed.
4. Celebrate Milestones
Reward yourself when you reach mini-goals. It keeps the process fun and motivating.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Setting Financial Goals
Even with good intentions, many people fall into common traps.
1. Setting Unrealistic Targets
Saying you’ll save half your salary overnight is setting yourself up for failure. Start small and grow gradually.
2. Not Writing Goals Down
Goals in your head get forgotten. Written goals have a higher chance of success.
3. Ignoring Inflation and Emergencies
Always leave room for unexpected costs or price increases.
4. Failing to Review and Adjust
Life changes. Your goals should, too. Revisit them every 6–12 months.
Tools and Apps to Help You Achieve SMART Financial Goals
| Tool/App | Use Case | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Mint | Budgeting and expense tracking | Beginners |
| YNAB (You Need A Budget) | Goal-oriented budgeting | Serious planners |
| PocketGuard | Automatic savings suggestions | Everyday users |
| Google Sheets/Excel | Custom goal tracking | DIY planners |
| Fidelity, Vanguard, Robinhood | Investment management | Long-term investors |
These tools help automate tracking so you can focus on execution instead of manual monitoring.
SMART Goals for Different Financial Situations
1. For Beginners
-
Save $1,000 in an emergency fund within 4 months.
-
Track all expenses for 30 days to identify savings opportunities.
2. For Families
-
Save $25,000 for a home down payment in 3 years.
-
Build a $5,000 education fund for your child within 2 years.
3. For Professionals
-
Invest $10,000 in diversified mutual funds over the next 12 months.
-
Pay off all credit card debt ($4,000) within 8 months.
4. For Retirees
-
Maintain a stable 4% annual withdrawal rate to preserve savings.
-
Rebalance investment portfolio annually.
Budgeting: The Backbone of SMART Goals
You can’t reach your financial goals without knowing where your money goes.
Here’s a simple budgeting formula:
50/30/20 Rule
| Category | Percentage | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Needs | 50% | Rent, utilities, groceries, transportation |
| Wants | 30% | Dining out, entertainment, hobbies |
| Savings/Debt | 20% | Savings, investments, debt repayment |
If your budget doesn’t allow for your SMART goals, look for ways to adjust:
-
Cut non-essential expenses.
-
Increase income through freelancing or side hustles.
-
Refinance or consolidate debts for lower interest rates.
SMART Financial Goals and the Power of Compound Growth
The earlier you start, the easier it gets — thanks to compound interest.
| Investment Example | Monthly Contribution | Annual Return (7%) | Duration | Final Amount |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scenario A | $200 | 7% | 10 years | $34,404 |
| Scenario B | $200 | 7% | 20 years | $98,925 |
| Scenario C | $200 | 7% | 30 years | $227,400 |
This simple table shows how time is your biggest financial advantage. The longer you invest, the faster your wealth grows.
Staying Motivated on Your Financial Journey
Reaching big financial goals takes time, patience, and consistency.
Here’s how to stay motivated:
-
Visualize Your Future – Picture your life once you reach your goal.
-
Track Progress Visually – Use charts or graphs to see your growth.
-
Find Accountability – Share your goals with a trusted friend or mentor.
-
Reward Yourself – Celebrate milestones responsibly (e.g., a dinner out after saving $1,000).
-
Stay Educated – Read about money, investing, and personal finance regularly.
Sample SMART Goal Worksheet (Template)
| Field | Example Entry |
|---|---|
| Goal | Build an emergency fund |
| Specific Target | Save $5,000 |
| Measurable | Save $417 per month |
| Achievable | Based on my $2,500 income and reduced expenses |
| Relevant | Helps me avoid credit card debt during emergencies |
| Time-bound | Complete within 12 months |
| Progress Check | Review savings monthly |
Use this format for each of your financial goals to stay clear and organized.
Pro Tips for Long-Term Success
-
Automate Everything: The less effort required, the better your consistency.
-
Track Net Worth: It’s the best way to measure overall financial growth.
-
Review Annually: Adjust goals as your life, income, or expenses change.
-
Educate Yourself: The more you learn about money, the faster you grow it.
-
Diversify: Never rely on one source of income or investment.
Final Thoughts: Take Control of Your Financial Future
Setting SMART financial goals is one of the most empowering steps you can take toward financial freedom. It transforms money from something that controls you into something you control.
Remember:
Financial success isn’t about luck — it’s about planning, discipline, and consistency.
Start small today:
-
Write down one specific goal.
-
Attach a number and deadline.
-
Track it for the next 30 days.
With time, those small wins compound into massive success.
Your future self will thank you for starting now.

